For installations of more than 200 users, a hardware strategy that separates the database server from the web (and possibly the application) server should be considered. It is not typically necessary to separate the servers unless you foresee one of the following:
There are many permutations of database server / web server / application server plus potential other components for load balancing that can be used in setting up an ExtraView network to support a large number of users. Here are some examples, together with a list of the important points to consider.

| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||
| Simple installation and configuration
Suitable for sites up to 1,000 users |
Not scalable for large numbers of frequent users
Not scalable for large number of concurrent connections No redundancy in case of failure (but consider using mirrored disk drives for redundancy) |
The following diagrams give examples of configurations. There are more possibilities and additional variants that can be configured, but it is unlikely they will give additional benefit to the ExtraView installation.
Variant 1: Web Servers and Application Servers on Single Computers 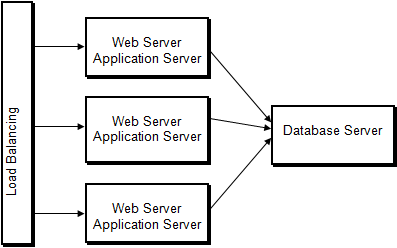
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||
| Scalable solution to handle a significant number of concurrent transactions
Redundancy with failure of a computer with the web and application server A single web or application server can be stopped for maintenance |
Expense of multiple web and application servers (although these each may be small, inexpensive computers)
Needs significant knowledge of server environments to set up and maintain |
Variant 2: Web Servers and Application Servers on Separate Computers 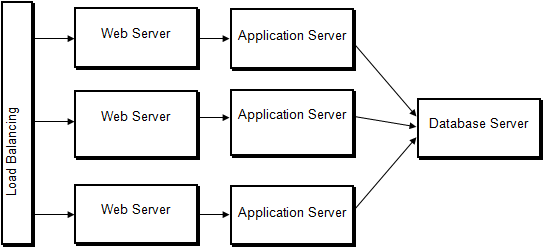
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |||
| Most scalable solution to handle a significant number of concurrent transactions
Redundancy with failure of a computer with the web and application server A single web or application server can be stopped for maintenance |
Expense of multiple web and application servers (although these each may be small, inexpensive computers)
Needs significant knowledge of server environments to set up and maintain |