The export creates a flat file containing the metadata in XML format. This file can be moved between different platforms and different instances of ExtraView. The order of objects in the file is defined by the requirements of ExtraView, not by the user. The data export is defined satisfying the requirements of being able to perform an import of the data, to build new objects. In short, all dependent data must follow the data upon which it is dependent.
There are a wide range of options, allowing you to perform exports of all or subsections of the metadata within an ExtraView installation.
Each option that defines a subset of the database is termed a family. This option is available from the Import/Export tab of administration.
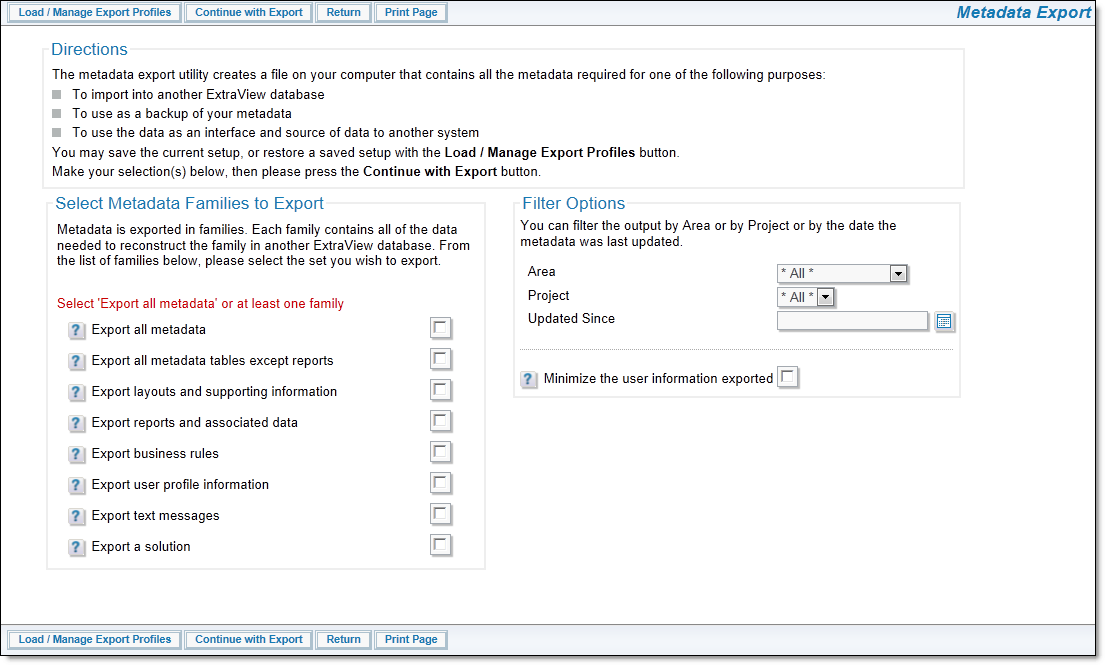
Exporting ExtraView Families
The following are the metadata families that may be exported. Note that any filters you set will also apply to the export file you create:
If you click the option Minimize the user information exported, then only the essential user information to export the metadata is written to the export file. This may solve a number of issues. For example, user information is often dynamic, and users may frequently change passwords, or administrators may activate and deactivate accounts on a production system or the references to the user information must always be taken from an LDAP or Active Directory server. While you may want the metadata from a development system to be migrated to a production system, you often may want to leave the production data related to users in place.
You may choose some overriding filters for the export. As opposed to exporting the data across all Business Areas and Projects, you may select a single Business Area and Project to export. You may also choose to only export data updated since a specific date and time.
Once you have set up an export profile, you may decide to save the combination for future use. This is accomplished through the Load / Manage Export Profiles button on the menu bar. This will display a popup as follows:
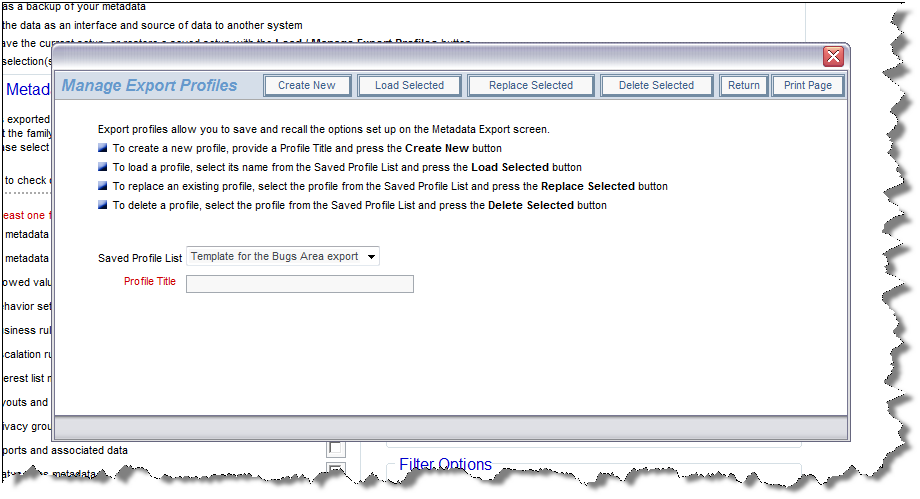
You may create new profiles and save them, load an existing template, replace an existing template or delete an existing template from the popup window. Once you have set up the profile to export, click the Continue with Export button. You are taken to a screen similar to this:
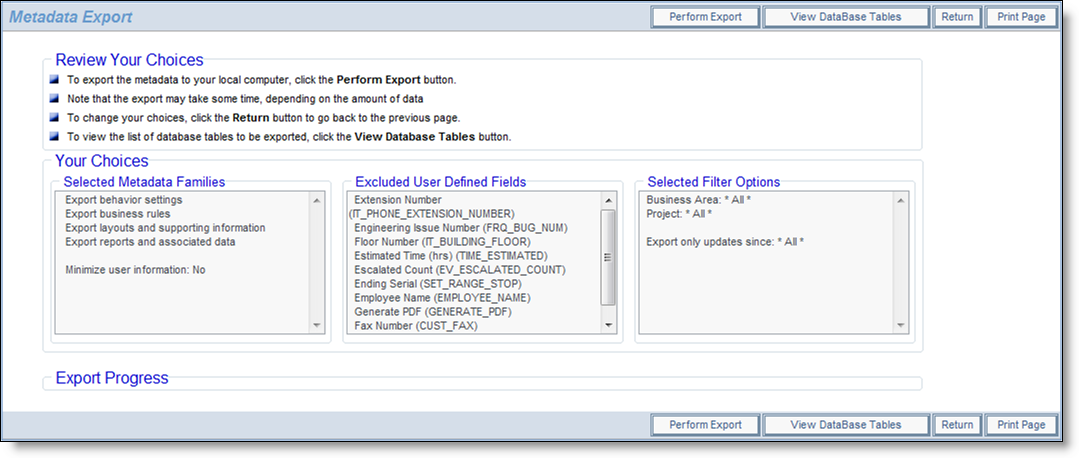
Continuing with the metadata export process
Confirm your choices on this screen, before clicking the Perform Export button.
You will be prompted to enter a file name for the export. This file will be saved on your local file system of your client computer.
An export can take some time, based upon the amount of metadata in your system. Files generated vary in size from a few to more than 50MB in size, dependent on the amount of metadata. As the export starts, one of the first steps is to compare the database against a known reference set of data that describes what the database should look like. In a perfect world, this step would not be needed, but databases can accumulate defects caused by any one of a number of factors. A previous update script might have failed, but the error not being noticed by the administrator; there might have been an incorrect command executed by a database administrator. There are other potential sources of failure as well. The metadata export process examines the database to ascertain if there is any obvious problem that will interfere with the process. The most typical problem encountered is that there is a missing database constraint. When a problem such as this is found, you will see an alert message warning of the event. You will be able to elect to continue, or to stop the process. It is recommended that you do not continue if you are not sure of the ramifications of the error.
An export file can be imported into the same or a different instance of ExtraView. The file can also be used to integrate with other applications.
There are a number of behavior settings that are not exported with this utility. This is deliberate, as it is most likely that these settings are specific to the target environment and may be different from those in the source environment. The list of settings that are not migrated is: