Selecting query filters will impose restrictions upon the report being produced and return a set of results that matches the filters you set. For example, if you select the Status Open, then only open issues will be displayed. Filters can be combined together, for example to show Open issues for the product named XXX that have been updated in the last 7 days.
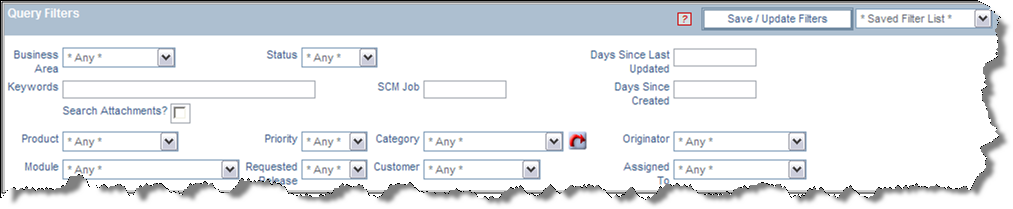
Saving filter sets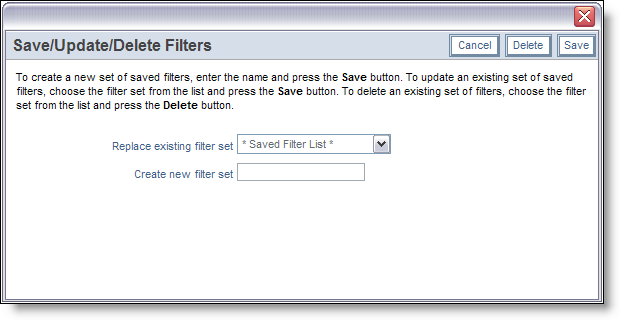
Dialog for saving filters
You may save any set of filters that you have defined, without making them part of a report. To achieve this, create the filters in either the Standard or Advanced mode as described below, then press the Save / Update Filters button. Within the popup window, you can either save the filters using a new name, replace an existing set of filters, or you can delete an existing filter set. The advantage is that you can quickly save and restore filter sets, using the Quicklist to display the results set.
The query filters change significantly, according to whether you are in Standard Query or Expanded Query mode.
This allows you to choose the values for fields, upon which records are selected for the report. There is a set of filters available directly on the Query / Report screen, as well as from the screens where you prepare or edit reports that you save for future use.
Typically, the Query / Report screen will show the most common filters you use, while the remaining screens show a more complete set of filters to which you have access. The fields available for your use are set up by your administrator.
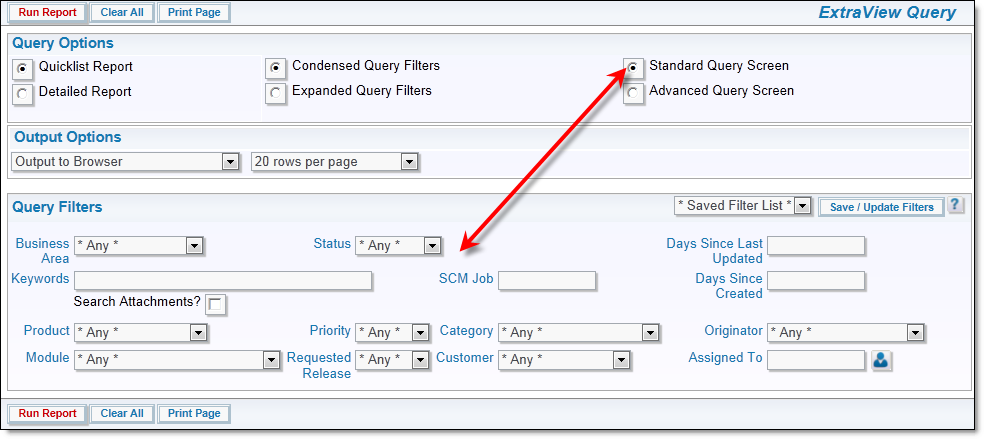
Standard query filters
If a query filter you select is the parent in a relationship, for example, the Module field may be dependent on the Product field, then the screen will refresh, and the child field will be populated with the valid entries for the parent you selected.
If your administrator has enabled the feature that allows you to search for inactive users, an additional prompt appears on the screen alongside the Query Filters heading. This is a checkbox with the label Show Inactive Users. When you check this, all the selection lists of users, will be refreshed, and will show inactive as well as active users, allowing you to perform searches for users who were at one time, but are not currently, licensed users of ExtraView. Note that this feature only works in Standard Query mode, and is not operable in Advanced Query mode.
If your administrator has given you access to advanced query mode, you first will select an individual field as the first filter to use in selecting individual records for the report. Then you select an operator such as “equals” or “greater than”, and then you select the value. For example, a filter may be:
Status not equal to Closed
You may add as many filters as you like, with each one beginning with a conjunction such as “and” or “or”. Advanced filters take a little longer to set up than standard mode filters, but they allow much more flexibility to create a complex set of query filters.
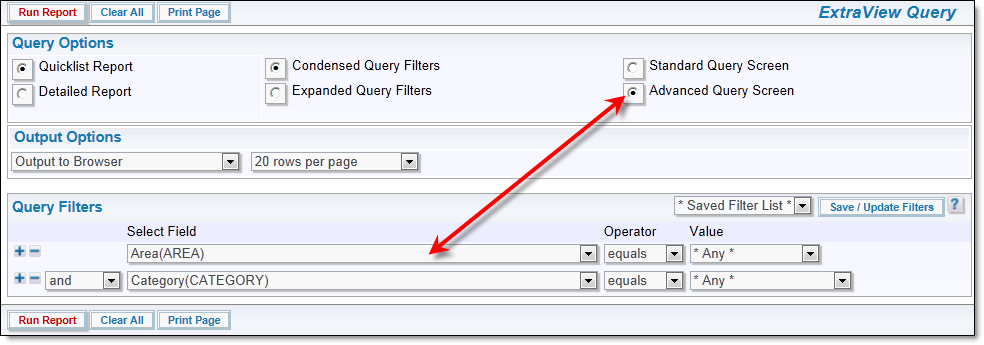
Advanced filter selection
To add a new filter, use the  button. Note that you can add filters following any existing filter. If you want to delete an individual filter from a query, use the
button. Note that you can add filters following any existing filter. If you want to delete an individual filter from a query, use the  button. This will eliminate the filter.
button. This will eliminate the filter.
In advanced mode, you can set the same filter field multiple times and use the “or” value. For example, you may set two filters as follows:
Priority equals P1 or Priority equals P2 |
Alternatively, you can use the Expanded search mode described below, and select multiple values from the Priority list.
The operators that appear in the drop down list are sensitive to the display type of the field you select. This allows you to select operators that only make sense and are eligible for each field display type. This table shows how this operates:
| Field display type | Operator values in Condensed Filter Mode |
Operator values in Expanded Filter Mode |
| Currency, Decimal, Number | Equals Greater than Less than Not equal Less than or equal to Greater than or equal to Empty Not empty |
Equals Greater than Less than Not equal Less than or equal to Greater than or equal to Empty Not empty |
| Checkbox, List, Pop-up, Tab, User | Equals Not equal |
Equals In Not equal Not In |
| Date, Day | Equals Greater than Less than Not equal Less than or equal to Greater than or equal to Between Empty Not empty |
Equals Greater than Less than Not equal Less than or equal to Greater than or equal to Between Empty Not empty |
| Keyword | Contains | Contains |
| Text Field | Equals Contains Not Equal Empty Not Empty |
Equals Contains Not Equal Empty Not Empty |
The operator values are largely self-explanatory, but a word of explanation is needed about the Empty and Not Empty values. When a numeric field (currency, decimal or number display types) is stored in ExtraView, and you do not enter a value, zero is not the value stored. A null, or empty value is stored and these are treated differently. Therefore searching for a value of empty will retrieve a different set of results that searching for a value of zero.
Also, note that for Checkbox, List, Pop-up, Tab and User fields when in Expanded Query mode, there are two additional operators, In and Not In. These allow you to define a list of values to search for that must be present or must not be present.
If you want to search for both empty and zero values, you may combine two filter conditions together, as exemplified by the following:
Amount Equals 0 or Amount is Empty
The following conjunctions can be used between the different filters of a report:
| Conjunction | Meaning |
| and | This filter will ensure that both filter conditions on each side of the and are true, before including the results |
| or | This filter will include results from the search, if either of the conditions on each side of the or is true |
| union | This will take the results of all the filters together preceding the conjunction union, together with the results of the filters in the query following the conjunction, and merge the results of both queries. For example, if you union two queries together, then you will see the results of both queries being returned on the report. The area within the red outline shows the results returned by two queries using the union conjunction.
|
| minus | This will take the results of the query filter(s) before the conjunction minus, and remove all results in common with the results of the query filter(s) following the conjunction. For example, if the query before the minus returns 100 rows, and the query following the minus returns 60 rows, 30 of which are to be found in the first part of the query, you will see 70 rows on the report that is generated. The area within the red outline shows the results returned by two queries using the minus conjunction.
|
| intersect | This will take the results of the query filter(s) before the conjunction intersect, and only display the results that are in common with the results of the query filter(s) following the conjunction. For example, if the first part of your query before the intersect returns 100 rows, and the second part of the query after the intersect returns another 100 rows, and 30 of the results are in both parts of the query, you will see these 30 rows returned on the report. The area within the red outline shows the results returned by two queries using the iintersect conjunction.
|
If your ExtraView installation is running on a Microsoft SQL Server database prior to the 2005 version or on the MySQL database0 not all the conjunctions are functional due to database limitations. Only conjunctions that are known to work are operable. Check with your administrator if you are not certain which database is used by your company.
If you have more than one union, minus or intersect conjunction in a query, then the filters up to the first one that contains the conjunction are grouped together.
The order in which you choose filters is significant if you choose to use the “or” conjunction in your query. The rules for parsing the queries are as follows, with the parentheses showing the precedence.
| Order of conjunctions | Significance |
| One “or” as the last filter | The condition in the filter with the “or” is used over the whole query. For example:
Product equals XYZ This query is parsed as follows: (Product equals XYZ (or Severity equals Severe ) |
| One “or” that is not the last filter | The “and” operators take precedence over the “or” operator. For example:
Product equals XYZ This query is parsed as follows: (Product equals XYZ (or Priority equals P 2 |
| There are multiple “and” and “or” filters | Once again, the “and” operators take precedence over the “or” operators. For example:
Product equals XYZ This query is parsed as follows: (Product equals XYZ (or Priority equals P 2 (or Severity not equal Major ) |
Note: You can toggle between standard search mode filters and advanced search mode filters at any time, but the filters currently on the screen are reset. Filters are not lost when you change between condensed and expanded filters.
Allowed values do not operate within filters selected for advanced queries. You will see all the parent and all the child values in the filter lists for these queries.
Within Advanced Search lists, an entry * Show disabled values * will appear in any list that contains values that have been disabled by the administrator. For example, you may wish to search for issues where the originator of the issue has left your company and their account has been disabled. If the field contains any values that are disabled, then you can select * Show disabled values * and the screen will refresh, showing all the disabled values. You can revert to only displaying enabled values with the prompt * Do not show disabled values * that will now be in the list.
On the Search/Report screen, you can type multiple issue ID’s into the Issue ID field. Separate these by a semicolon ‘;’.
There are occasions when it is useful to be able to search for a null value, or the absence of a value. For example, you may want a report where the filter is to be “show me all the records that have an empty customer field”. If the field is a list field, you can select the entry * None *. If the field is a text field, however, you can enter the character string {null}, to signify that you are looking for a null.
User fields have two options related to their ability to search, using the selected value or values as filters. First, there is an entry within the search list, * Current User *. When this entry is selected, the name of the user currently signed in is used as the filter value. If your administrator has enabled the option, there may also be an entry in the list, * Include Inactive Users *. By default, each list of users only includes activated users. When you select this option, the screen refreshes and the user list will include both active and inactive user names.
If your installation uses pop-up selection for users, a checkbox will allow any search you make, to include inactive user names.